In this tutorial, we will look at how to configure the firewall on Proxmox.
In general, configuring the firewall on any device is extremely powerful since you’re able to limit connections to specific IP addresses or subnets. With Proxmox, it’s even more powerful considering there are various virtual machines and containers that are generally configured on one device. If you’d like to limit access, using Proxmox’s firewall feature will allow you to do just that.
We will look at how to configure the Firewall on Proxmox below using the Datacenter, Node, or VM/Container options!
How to Configure the Firewall on Proxmox
Before we look at how to configure the firewall on Proxmox, I want to give a few disclaimers:
- There are technically three types of firewall configurations that you can use on Proxmox, but they all operate the same (Datacenter, Node, or VM/Container). A few additional notes about this configuration:
- Creating rules for the Datacenter will apply to Nodes under the Datacenter, however, they will not apply to VMs or containers under the Datacenter or Node.
- Creating a firewall rule for a specific Node will not apply to the Datacenter, VMs, or Containers. Node rules will only apply to the Node individually.
- Until the firewall is enabled, none of the firewall rules will apply! Therefore, when you’re comfortable that the base rules you need to access your services are created (at minimum), you can enable the firewall to begin using it.
- As soon as the firewall is enabled, it will block all traffic by default, meaning that anything attempting to access a port that hasn’t had an allow rule created for it will be blocked!
- The exception to this is if you change the default Input Policy (Firewall > Options > Input Policy). If you change the Input Policy to Accept, you must create firewall rules for services you’d explicitly like blocked.
Proxmox Ports
The ports used by Proxmox v6 and above are listed below.
- Web interface: 8006 (TCP, HTTP/1.1 over TLS)
- VNC Web console: 5900-5999 (TCP, WebSocket)
- SPICE proxy: 3128 (TCP)
- sshd (used for cluster actions): 22 (TCP)
- rpcbind: 111 (UDP)
- sendmail: 25 (TCP, outgoing)
- corosync cluster traffic: 5405-5412 UDP
- live migration (VM memory and local-disk data): 60000-60050 (TCP)
This is extremely important to take note of because if you’re using the Proxmox Firewall, you might have to create rules for some or all ports above.
NOTE: The list above has been taken directly from the official Proxmox page.
Why Configure the Firewall on Proxmox?
Configuring the firewall on Proxmox is a great way to enhance the overall security of Proxmox. Since Proxmox hosts multiple virtual machines (VMs) and LXC containers that could potentially be targeted, configuring Proxmox firewall rules that do/do not permit access is important.
The firewall on Proxmox serves as a critical “line of defense”, controlling inbound and outbound network traffic based on predetermined firewall rules. It helps block unauthorized access which protects your VMs and the data contained within them.
Also, if you have VMs exposed to the internet (such as web servers or remote access portals), the firewall on Proxmox is absolutely necessary to help mitigate the risk of cyber threats. While it’s best to configure a DMZ in scenarios like this, the Proxmox firewall is something that can easily be completed that offers strong protection.
Finally, Proxmox firewall rules can also provide better overall network performance since it permits or blocks specific types of traffic, improving your overall network and system performance.
Datacenter Proxmox Firewall Configuration
1. The first rule that we will create is to access the Proxmox GUI. This rule will be created for port 8006 and will apply at the Datacenter level. Select Datacenter, then Firewall, then Add to create a new rule.
NOTE: You will need the interface name to create the firewall rule. This can be found by selecting a Node, then Network, and finding the name of the interface. In my case, it’s vmbr0, but you should confirm before enabling the firewall.
In a recent update to Proxmox, the GUI and SSH ports have been allowed by default, meaning that you shouldn’t be able to lock yourself out of either. However, I’d still recommend creating a rule for each at the Datacenter level!
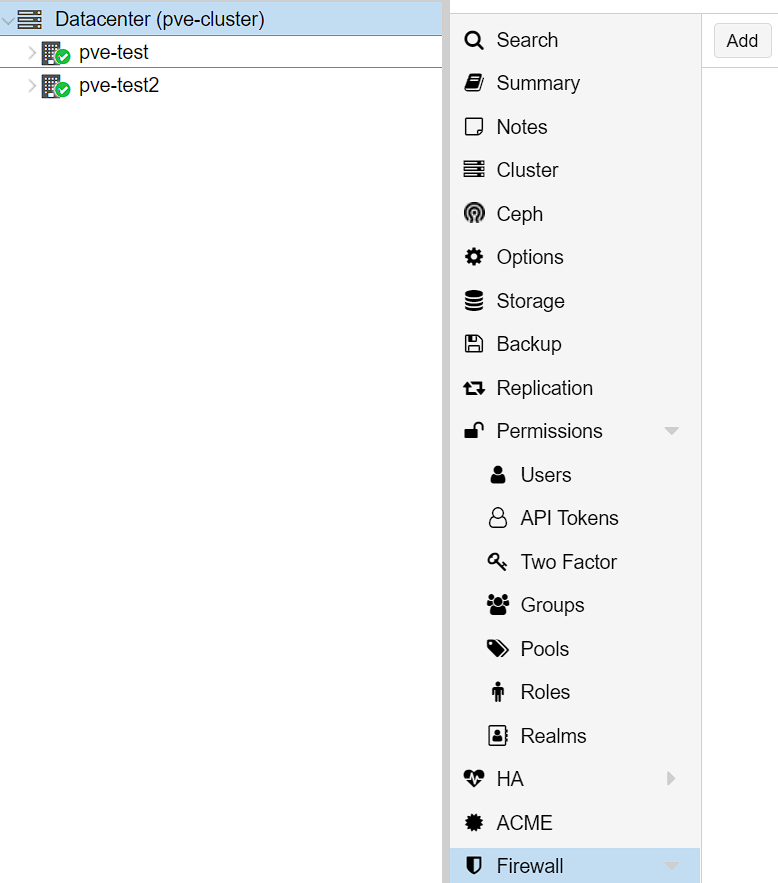
2. Set the Interface to be the interface name your Proxmox server is using (mind is vmbr0), set the Protocol as TCP, then set the Destination Port as 8006. Make sure it’s enabled, then select Add.
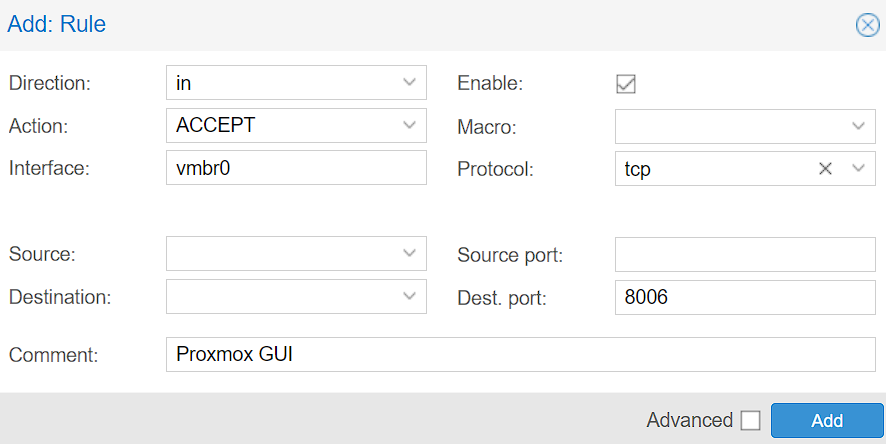
NOTE: I’d recommend creating a second rule for port 22 (SSH) so that you can access Proxmox through the Web GUI or SSH.
3. From a bare minimum perspective, the rule(s) above will allow you to access the Proxmox GUI (and SSH if you created a rule for it), however, the rule(s) can be modified by specifying a specific source IP address or subnet. This will ensure that the IP address or subnet specified are the only devices that can access this specific port.
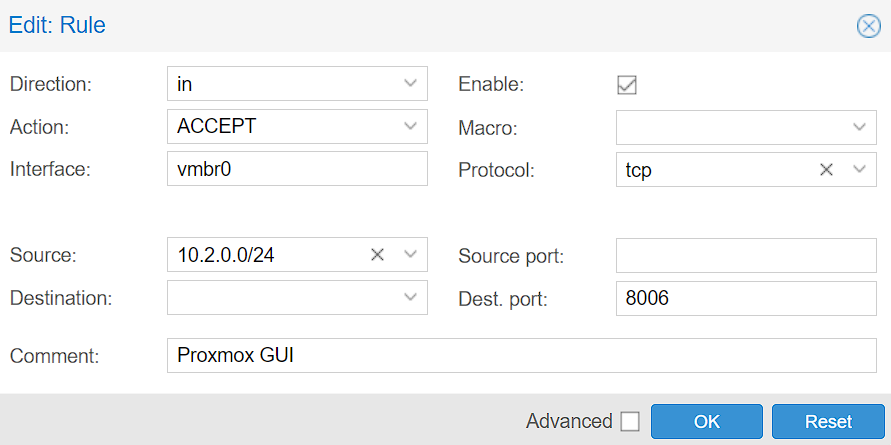
4. As mentioned above, the firewall will not be enabled until you actually enable it. To enable it, select Options under Firewall, then Edit the Firewall, then enable it and select OK.
NOTE: This will enable the firewall, so if you have not set up the correct firewall rules, services can be blocked!
Node Firewall Configuration – How to Configure the Firewall on Proxmox
The Node Firewall Configuration is the exact same as the Datacenter Firewall, but rules will only apply to the Node specified. Therefore, if you have multiple Nodes in a cluster and would like them to have different firewall rules, it’s best to specify them on a Node level, rather than a Datacenter level. Please keep in mind that you must have the firewall enabled at the Datacenter level to use it on the Node!
As mentioned above, Nodes will inherit firewall rules from the Datacenter. Therefore, if you only have an individual Node or would like all Nodes to have the same firewall rules, you should specify them at the Datacenter level.
With that said, VMs or Containers will not inherit firewall rules from the Node they’re currently on! For that reason, you must create firewall rules for each VM/Container individually!
Virtual Machine/Container Firewall Configuration
As mentioned above, VMs/Containers will not inherit firewall rules from the Node they are on. For this reason, individual firewall rules must be created for each VM/Container if you’d like to use it.
NOTE: The Firewall MUST be enabled at the Datacenter level for the Firewall to work at the Node/VM level!
1. Create Firewall Rules on the individual VM or Container by selecting it, selecting Firewall, then Add.
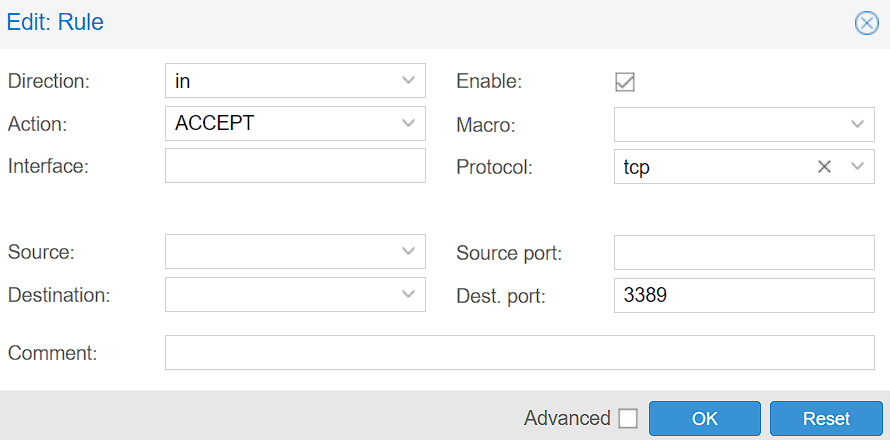
2. Create the Firewall Rule by specifying the Protocol and Destination Port. Make sure the rule is created, and select OK to create the firewall rule.
NOTE: the rule(s) can be modified by specifying a specific source IP address or subnet. This will ensure that the IP address or subnet specified are the only devices that can access this specific port.
The rule below allows RDP to a Windows 11 Virtual Machine.
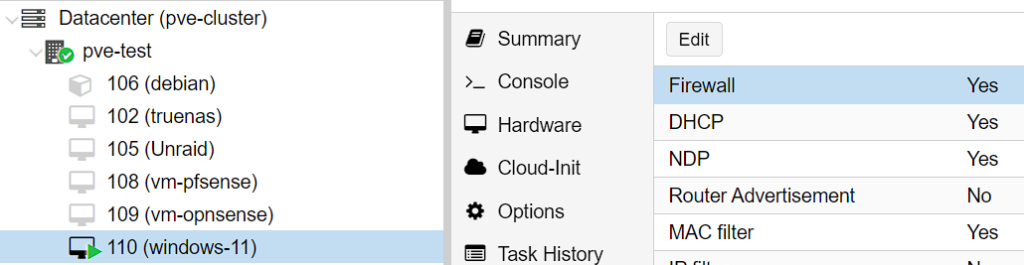
3. When the Firewall rules have been created, edit the Firewall Options and ensure that it’s enabled (Firewall > Options > Firewall > Yes). After it has been enabled, the Firewall rules will apply!
Conclusion: How to Configure the Firewall on Proxmox
This tutorial looked at how to configure the firewall on Proxmox. This process is slightly confusing because there are technically three different sections where you can create Firewall rules (Datacenter, Node, VM/Container).
As soon as you understand that Nodes will inherit Datacenter rules, but VMs/Containers will not inherit Node rules, it starts to get a little easier to understand and you can begin creating the correct firewall rules. Just make sure you enable the firewall and specify the correct firewall rules for each!
Thanks for checking out the tutorial on how to configure the firewall on Proxmox. If you have any questions on how to configure the firewall on Proxmox or really any Proxmox Firewall questions, please leave them in the comments!




