This article will look at the difference between the Btrfs vs. Ext4 file systems. Btrfs and Ext4 are Linux file systems but are extremely different. Btrfs has advanced features like Snapshots, data integrity verification, and built-in RAID support.
Alternatively, Ext4 has benefits like stability, performance, and reliability (from being a tried and tested filesystem). We’ll compare Btrfs vs. Ext4 in further detail below to determine which file system is best! Before looking at Btrfs vs. Ext4, let’s look at exactly what each file system offers users.
What is a File System?
A file system manages the way data is organized, stored, and retrieved. This ensures the data is managed properly and helps from a data integrity perspective.
Selecting the correct filesystem can sometimes be confusing (especially on certain operating systems), so we’ll break down Btrfs vs. Ext4 below to highlight the main differences.
Btrfs: Detailed Overview
Btrfs is a modern file system designed for Linux which prioritizes data integrity, fault tolerance, and easy administration. Btrfs supports advanced features like snapshots, built-in RAID, and copy-on-write, making it a great choice for various storage applications.
Btrfs Features
Here are some of the key features of Btrfs:
- Copy-on-Write (CoW): Btrfs uses CoW, which means that when a file is modified, only the changes are written to a new location, leaving the original data intact.
- Snapshots: Btrfs can create snapshots of the file system, which are point-in-time copies of the data. These snapshots can be used for backups or to roll back changes.
- Data Integrity: Btrfs uses checksums for both data and metadata, which is used for data integrity and helps detect and fix errors.
- Built-in RAID Support: Btrfs supports various RAID levels, including RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 10, and RAID 5/6.
The chart below shows some common Btrfs RAID configurations:
| RAID Type | Redundancy |
|---|---|
| RAID 0 | No redundancy; data loss if a device fails. |
| RAID 1 | Provides redundancy; can tolerate the failure of one hard drive. |
| RAID 10 | Provides redundancy; can tolerate the failure of one hard drive per mirrored pair. |
| RAID 5 | Provides redundancy; can tolerate the failure of one hard drive. |
| RAID 6 | Provides redundancy; can tolerate the failure of two hard drives. |
An extremely common system where users may be running Btrfs is on NAS devices (especially if using RAID as shown above). There are various NAS operating systems that support Btrfs (like Unraid, or Synology DSM, shown below).
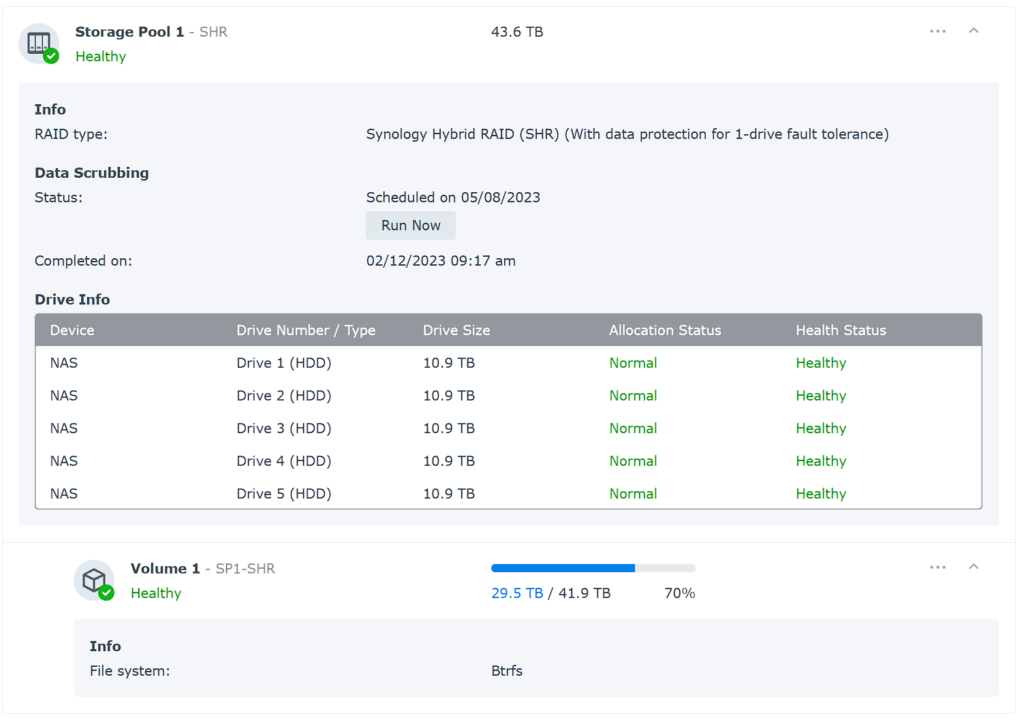
While Btrfs doesn’t have automatic repair capabilities (using a Synology NAS as an example), you can use a data-scrubbing process that will repair data integrity issues.
Btrfs Performance
In terms of performance, Btrfs is exceptional when using it with large files and large volumes. However, it can be slower for small file writes due to its Copy-on-Write nature.
Who Should Use Btrfs?
Btrfs is ideal for users who require advanced features like snapshots, data integrity checks, and built-in RAID support. It’s well-suited for home NAS setups, servers, and scenarios where data protection is a high priority.
Ext4: Detailed Overview
Ext4 is the default file system for many Linux distributions and is extremely popular. Introduced in 2008, Ext4 is an improved version of its predecessor, Ext3, and offers better performance, reliability, and scalability.
Ext4 Features
Here are some of the key features of Ext4:
- Backward Compatibility: Ext4 is backward compatible with Ext2 and Ext3.
- Journaling: Ext4 uses journaling to ensure file system consistency which is helpful in unexpected events like system crashes or power failures.
- Large File System Support: Ext4 can support volumes up to 1 exbibyte (EiB) and individual files up to ~6.6 terabytes (TB).
- Extents: Ext4 uses extents, which is a set of blocks that are contiguous within a file. This improves performance and reduces fragmentation.
Ext4 Performance
Ext4 is generally faster than Btrfs for everyday tasks, thanks to its faster codebase and optimization for common workloads. It performs well with small file writes and is known for its stability and reliability.

Who Should Use Use Ext4?
Ext4 is used in a bunch of different scenarios like desktop devices and servers as it provides exceptional performance and stability.
It’s a great option for users who want a reliable file system without requiring special features like RAID support of snapshots.
What is the Main Difference Between Btrfs and Ext4?
The biggest difference between Btrfs and Ext4 is that Btrfs is designed to be used with advanced data features like snapshots and data integrity checks. Ext4 is designed for great performance and reliability.
Here are a few other differences:
- Features: Btrfs has more advanced features, such as snapshots, data integrity checks, and built-in RAID support. Ext4 focuses on providing a reliable and stable file system with good performance.
- Performance: Ext4 performs better in everyday tasks and is faster for small file writes. Btrfs excels when working with large files and large volumes, but its Copy-on-Write functionality can sometimes cause slowdowns in small file writes.
- Stability: Ext4 is known for its stability and reliability, making it the default choice for many Linux distributions. In general, Btrfs is not as stable as Ext4, though it offers features that Ext4 doesn’t.
Conclusion: Btrfs vs. Ext4
This article looked at Btrfs vs. Ext4. In general, if you’re using a NAS device, you most likely want to use Btrfs for its snapshot and data integrity features. While Ext4 is an option, those are important features that you’ll be missing.
While that is the case for NAS devices, there is an exception and it’s performance. If you’re looking to build the most performant NAS possible, go with Ext4. In individual operating system scenarios, the common choice for most will be Ext4 as well.
Thanks for checking out the article on Btrfs vs. Ext4. If you have any questions on Btrfs vs. Ext4, please leave them in the comments!




