Which CMR vs SMR hard drive is better, and which should you use? Most people seek the answer to this when purchasing the right hard drive to meet their storage needs. This article will help you understand more about these two types of hard drives to help you choose the best one.
An HDD (hard disk drive) is a data storage option that utilizes mechanical parts, unlike an SSD (solid-state drive) that utilizes flash memory. Most people fail to understand that different forms of magnetic recording happen on hard disk drives.
Both CMR (conventional magnetic recording) and SMR (shingled magnetic recording) are technologies used to physically store data on hard drives. CMR drives store data on individual tracks whereas SMR drives store data in overlapping tracks with subsequent data tracks on the hard disk being partially overwritten when new data is written.
This article will provide a full CMR vs SMR hard drive comparison to help you make an informed decision.
Some links below are Amazon affiliate links which means that I earn a percentage of each sale at no cost to you. Thank you for your support.
What is a CMR Hard Drive?
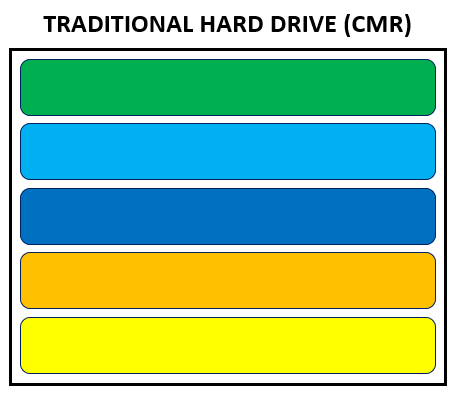
CMR stands for Conventional Magnetic Recording, previously known as PMR (Perpendicular Magnetic Recording). Since PMR is also used with SMR hard drives, CMR has been chosen to better distinguish between the two types.
With CMR technology, the data is written to free areas of the hard disk without existing data having to be rewritten or moved. Magnetization is carried out horizontally and vertically on plates. It is possible to write directly to the final data storage location on the hard drive without the data being written back to the hard drive first.
The write performance of CMR hard drives is, therefore, usually better. The difference in performance between CMR and SMR becomes greater the more data is written and the less free storage capacity the hard disk has.
Click here for our favorite CMR hard drives: Seagate IronWolf Pro and Western Digital Red Pro.
What is an SMR Hard Drive?
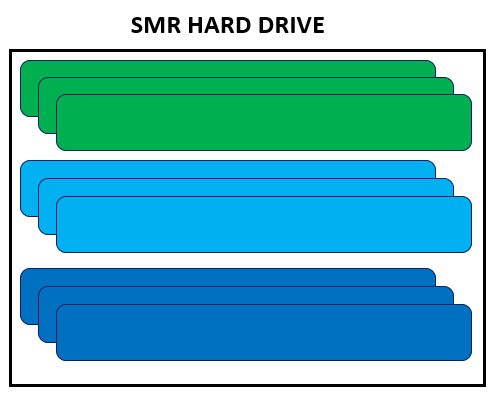
SMR stands for Shingled Magnetic Recording and describes a technique in which the write head of the hard disk is larger than the read head. This allows data to be stored on the hard disk in an overlapping way, with subsequent data tracks on the hard disk being partially overwritten when new data is written. This saves space and allows a significantly higher capacity with the same platter size.
In an SMR disc, the write head is larger and less watermarked than the read head. This makes it possible to partially overlap the tracks and thus write more data to disk. The problem is that when the hard disk writes data, it must also write the tracks that overlap it again while their data is unchanged.
With a cache system, this is almost transparent. However, the transfer rate may drop with large files after a certain amount of data because the cache is full and must be cleared first.
Click here for our favorite SMR hard drive: Western Digital Red
CMR vs SMR: Benefits and Drawbacks
There are some benefits and drawbacks when comparing CMR vs SMR hard drives that must be considered before purchasing one. The information below will guide you in making the correct decision based on your requirements.
CMR Hard Drive Benefits
CMR hard drives are the best choice for active storage. For example, when data must be read and written at high transfer rates or with enormous amounts of data. This is the preferred hard drive in NAS devices, especially when there is a redundancy mechanism.
It is also ideal for use in several activities, such as:
- Video, audio, or image processing for use on NAS servers or general-purpose servers
- Music streaming
CMR Hard Drive Drawbacks
- A CMR hard drive is more expensive than an SMR hard drive.
SMR Hard Drive Benefits
- The advantage of this technology is that the storage density is increased (up to 30% more). SMR drives offer greater storage capacity and are more energy-efficient than CMR drives.
- SMR hard drives are a good choice if used primarily for data archiving. For example, writing the data once and occasionally accessing it. This can be used for photo and video archives that you keep for a very long time. However, the use of SMR hard drives in NAS devices, especially when a redundancy mechanism (RAID) is used, is not recommended.
SMR Hard Drive Drawbacks
- When new data is written, older data already on the hard disk often has to be moved as well, as this is partially overlapped by new data and then becomes partially illegible. Therefore, some older data must also be rewritten and can, in turn, overwrite other data. To ensure this doesn’t cause all data to be rewritten on hard disks with high-capacity utilization, the data is divided into groups or bands that are managed together.
- With many small movements and changes, this behavior can increase to such an extent that the hard disk cannot move data fast enough and, for example, exits a RAID with an error. This can happen with a RAID rebuild, in which a large amount of data has to be rewritten.
For the reasons above, you should not use SMR hard drives with RAID.
Main Difference Between CMR and SMR Hard Drives
The main difference between CMR and SMR hard drives is the data storage method that they both use. CMR uses parallel, non-overlapping tracks, and SMR uses overlapping tracks. CMR hard drives are better for usage in RAID arrays and are considered better overall drives, with SMR hard drives providing better results for archive purposes and performing poorly for RAID Arrays.
Here are some other key differences comparing CMR vs SMR hard drives:
| Feature | CMR (Conventional Magnetic Recording) | SMR (Shingled Magnetic Recording) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Storage Method | Parallel tracks, non-overlapping | Overlapping tracks, like shingles |
| Storage Density | Lower density, less storage capacity | Higher density, more storage capacity |
| Write Performance | Consistent and faster write performance | Slower write performance, especially for random writes |
| Read Performance | Comparable read performance | Comparable read performance |
| Use Cases | General-purpose storage, various workloads | Archival storage, workloads with less frequent writes |
| Compatibility | Compatible with most applications and workloads | May require workload-specific optimizations |
| Cost | Varies, generally more expensive per terabyte | Varies, generally cheaper per terabyte |
Should You Choose a CMR or SMR Hard Drive?
You should identify your backup and storage needs to know the best hard drive for you based on this CMR vs SMR comparison. Generally, an SMR hard drive will provide you with the same capacity as a CMR hard drive at a lower price per disk. The main disadvantage is that it will be less flexible in use.
SMR drives give you random-read capabilities for quick data access like CMR drives. Still, they are ideal for custom systems that utilize their structure and high capacity since they need continuous workloads and a lot of idle time for the best performance.
You should use an SMR hard drive for archiving and backup because less frequent drive access creates room for improved drive performance at an affordable cost. Businesses that want to buy high-capacity drives opt for SMR drives because they offer a similar capacity on fewer drives.
Conclusion: Go for a CMR Drive
After comparing CMR vs SMR hard drives, you should opt for a CMR drive for almost all circumstances outside of archiving and backups from an individual device.
Businesses that need storage to operate 24/7 with minimal downtime and to store a huge number of files should opt for a CMR hard drive. This helps to ensure the quick and secure addition of data. Most CMR drives are meant for NAS environments. They can easily manage heavy workloads without dropping performance or slowing down.
Most manufacturers like Seagate indicate the technology used in their hard disks. When buying a hard drive, check the datasheet for the writing method used. You can consult your vendor or other experts for brands that aren’t indicated.
If you’re interested in buying a CMR hard drive for RAID usage, these are two hard drives that we recommend: Seagate IronWolf Pro and Western Digital Red Pro. Both of these devices are CMR hard drives that come with 5-year warranties.
If you’re certain that you’d like an SMR hard drive, click here for our favorite: Western Digital Red. Thanks for checking out the article on CMR vs SMR hard drives!





